Half a billion adolescents could face obesity by 2030, report warns
A Lancet commission report warns that by 2030, 464 million adolescents will be obese or overweight. It highlights a global crisis in adolescent health, mental well-being, and climate-related risks, calling for urgent policy action.
-
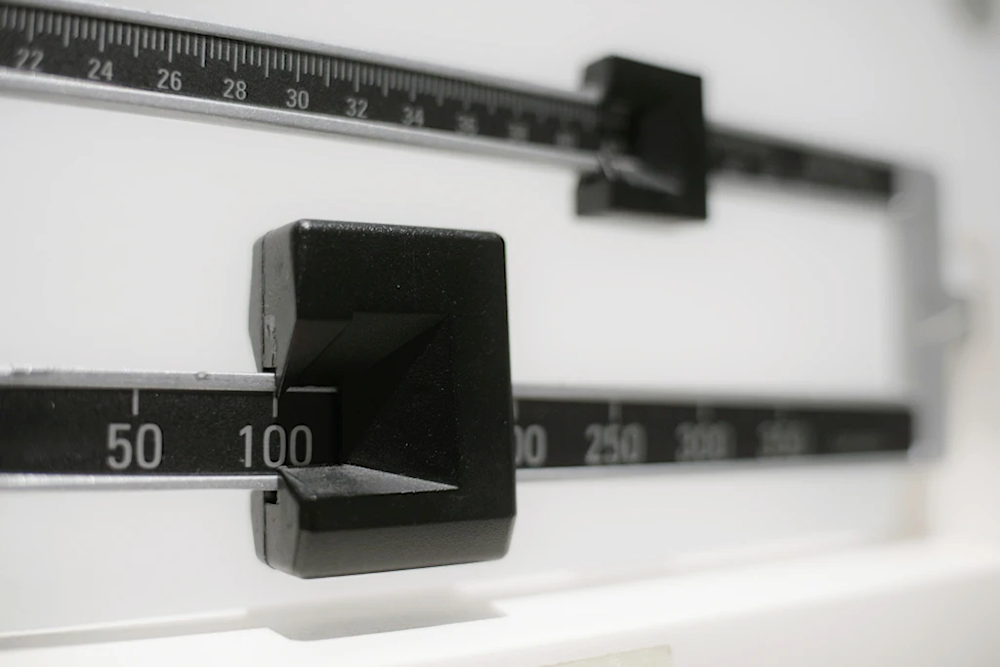

A beam scale is seen in New York on April 3, 2018. (AP/Patrick Sison)
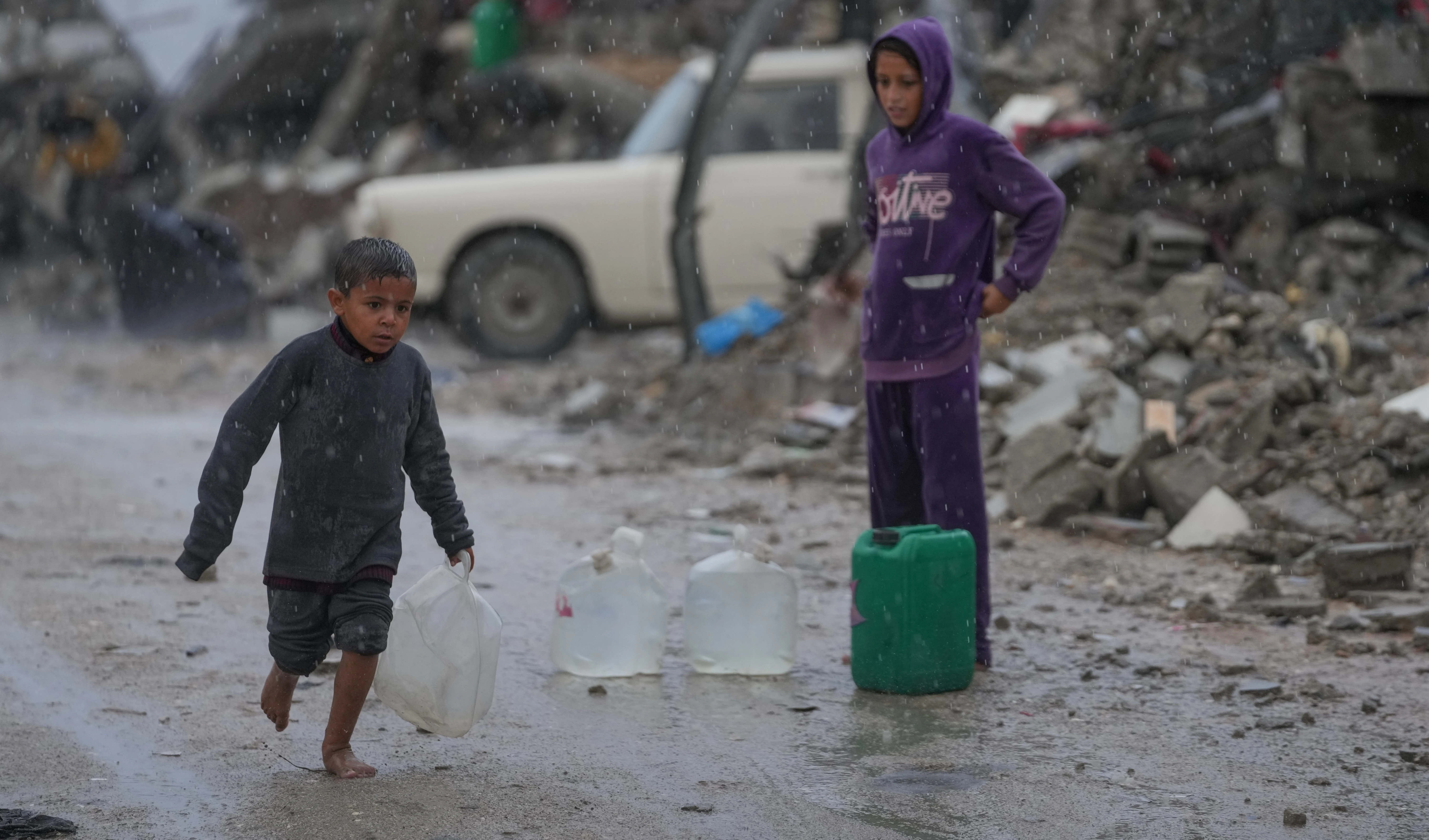
Nearly half a billion adolescents worldwide will be living with obesity or overweight by 2030, with one billion at risk of preventable health issues, according to a new international report from the Lancet Commission on adolescent health and wellbeing. The authors warn that global adolescent health is at a "tipping point," demanding urgent action.
While adolescent mortality has declined by over 25% in the past two decades, the report projects that by 2030, 464 million adolescents aged 10 to 24 will be obese or overweight, an increase of 143 million from 2015. The burden of adolescent obesity is particularly severe in high-income countries, Latin America, the Caribbean, North Africa, and the Middle East, where over a third of young people are already affected.
The commission also raised concerns about a “significant decline” in adolescent mental health, highlighting that young people face growing threats from preventable health problems, including HIV/AIDS, early pregnancy, depression, and malnutrition. These challenges, the authors stress, are now part of daily life for youth in more than half of the world’s countries.
Climate change has emerged as another major threat to adolescent health. According to the report, today’s youth will be the first generation to live their entire lives under worsening climate stress, exposing them to extreme weather, food and water insecurity, and heat-related illnesses. The study estimates that by 2100, around 1.9 billion adolescents will be impacted by the long-term effects of global heating.
Despite progress in reducing substance abuse and improving youth engagement in education and work, the report finds these gains are being undone by chronic underfunding and the lasting effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. The authors note a significant decline in the number of young people smoking or drinking alcohol globally and improvements in school and employment participation, but these advancements have been undermined by broader systemic challenges.
Global failure to act risks creating a 'lost generation' of unhealthy adolescents
Professor Sarah Baird of George Washington University, co-chair of the Lancet Commission, stated, “The health and wellbeing of adolescents worldwide is at a tipping point … Investing in the health and wellbeing of young people is crucial for safeguarding our collective future.”
The report concludes that without decisive political will, comprehensive policy changes, and financial investment, the world will see a growing population of adolescents living with obesity and other preventable health problems. Failure to act, the authors caution, will result in a lost generation facing long-term health risks.
Dr. Anshu Banerjee, Director of Maternal, Newborn, Child and Adolescent Health and Ageing at the World Health Organization, emphasized the need for global collaboration. “From ending child marriage to tackling the mental health crisis and obesity, we must confront both old and emerging threats to their health. These problems do not know national boundaries, neither should our solutions.”
Our June 2025 issue is now live with content on managing glycaemic abnormality in #CysticFibrosis, predicting the severity of community-acquired #Pneumonia, real-world & long-term effectiveness of nirsevimab for #RSV, & more 👉https://bit.ly/3FjByaz #MedSky #PedSky #IDSky #EndoSky
— The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health (@lancetchildadol.bsky.social) May 19, 2025 at 4:48 PM
[image or embed]
Johanna Ralston, CEO of the World Obesity Federation, echoed the urgency, calling adolescent obesity a product of failing systems. “The rise in obesity and related diseases is not just a matter of individual choices, it’s the result of environments flooded with health-harming products including ultra-processed food, alongside policies that fail to protect young people.”
The commission’s findings make it clear: without immediate and coordinated global action, adolescent health will continue to deteriorate under the combined pressure of obesity, poor mental health, climate disruption, and under-resourced health systems.

 4 Min Read
4 Min Read