Rwandan, Congolese leaders to meet over eastern DRC conflict
The M23 armed group is escalating its hostilities as the leaders of Rwanda and the DRC seek to hold talks with the hopes of ending the devastating conflict.
-
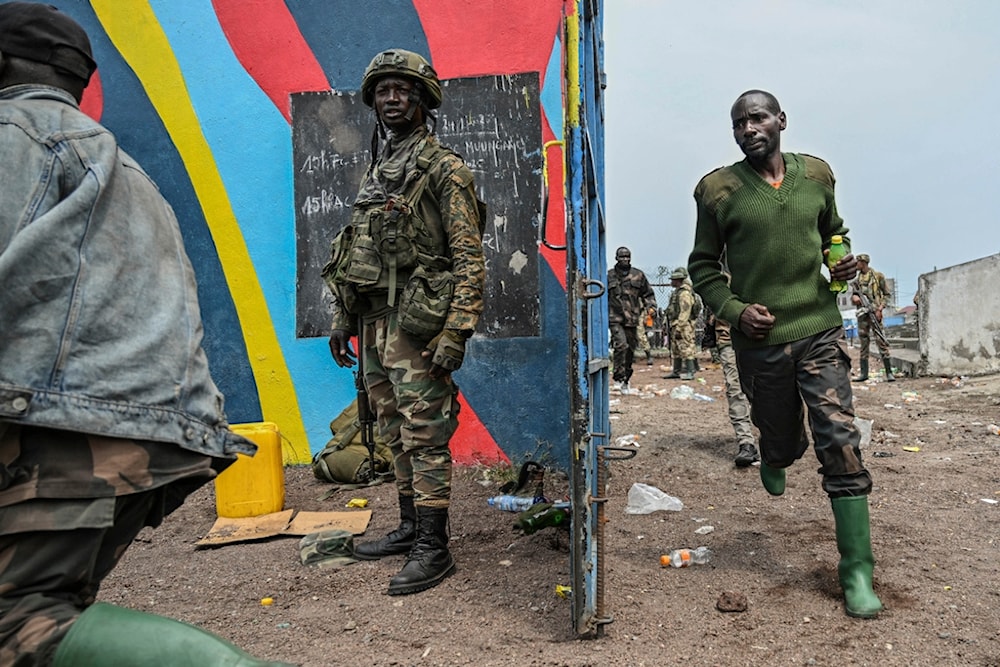

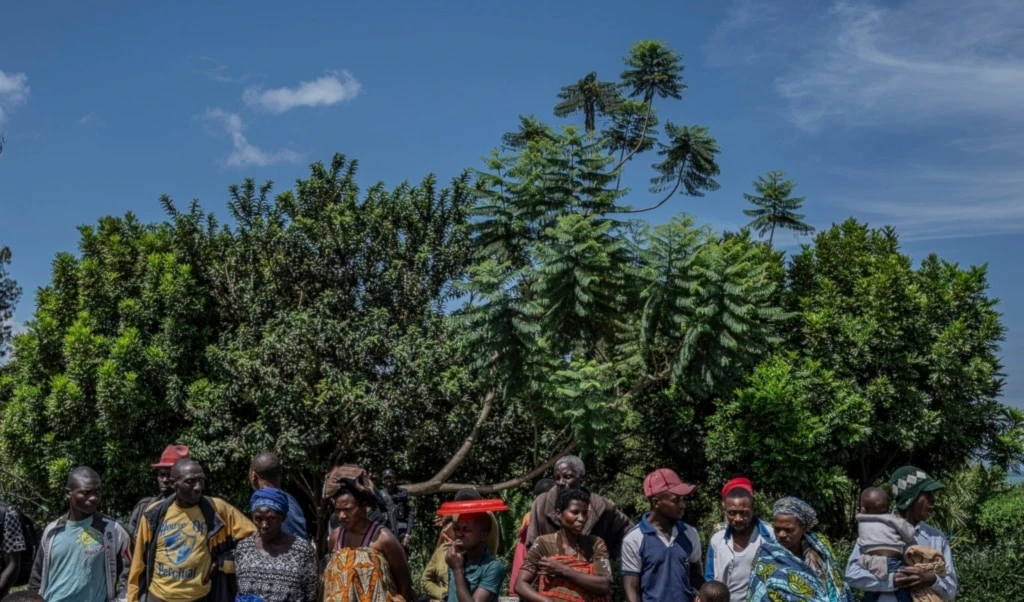
Government soldiers and police officers who surrendered to M23 rebels, center, run to board trucks to an undisclosed location in Goma, Democratic Republic of the Congo, on Thursday, January 30, 2025. (AP)
Rwanda's President Paul Kagame and his Congolese counterpart Felix Tshisekedi are set to meet in Tanzania on Saturday as regional leaders convene in an effort to defuse the ongoing conflict in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).
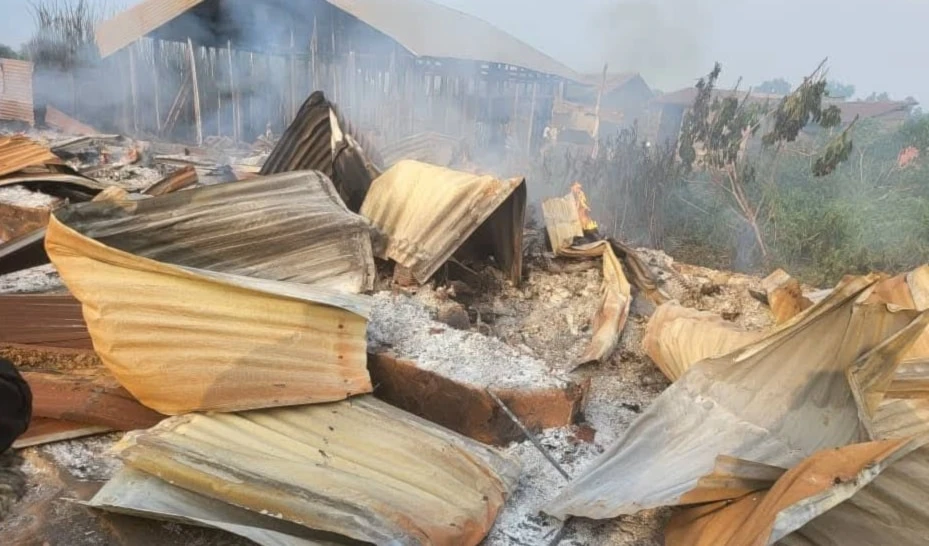
The Rwanda-backed M23 armed group has rapidly seized swathes of territory in the mineral-rich eastern DRC, launching an offensive that has left thousands dead and displaced large populations. Last week, the group took control of the strategic city of Goma and is now pushing into neighboring South Kivu province, intensifying the decades-long turmoil in the region.
Kagame and Tshisekedi will attend a joint summit in Dar es Salaam, bringing together the eight-member East African Community (EAC) and the 16-nation Southern African Development Community (SADC).
Since the M23 resurfaced in 2021, multiple peace talks hosted by Angola and Kenya have failed to secure lasting stability. Rwanda has denied providing military support to the group, but a UN report last year alleged that Rwanda had deployed around 4,000 troops in the DRC and was profiting from smuggling gold and coltan—key minerals used in electronic devices—out of the country.
Meanwhile, Rwanda accuses the DRC of sheltering the Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda (FDLR), an armed group founded by ethnic Hutus involved in the 1994 Rwandan genocide against the Tutsi population.
Mounting concerns over M23
As the summit convenes, the M23 is advancing on the town of Kavumu, home to an airport crucial for supplying Congolese troops. Kavumu serves as the last barrier before the provincial capital Bukavu, a city bordering Rwanda, where panic has escalated.
"The border with Rwanda is open but almost impassable because of the number of people trying to cross. It's total chaos," said a Bukavu resident, adding that businesses were barricading their storefronts and educational institutions had suspended classes.
UN human rights chief Volker Turk warned of worsening conditions in the region. "If nothing is done, the worst may be yet to come—for the people of eastern DRC, but also beyond the country's borders," he stated.
Turk reported that nearly 3,000 people have been confirmed killed and 2,880 injured since M23 seized Goma on January 26, though actual numbers are likely higher. His office is also investigating allegations of sexual violence, including rape, gang rape, and sexual slavery.
Expanding authority
The M23 has already installed its own mayor and local administration in Goma and has declared its intent to march on the national capital, Kinshasa—despite it being roughly 1,600 km away. The DRC army has been forced into multiple retreats.
The offensive has sparked concerns of a broader regional war, as several nations, including South Africa, Burundi, and Malawi, are actively supporting the DRC militarily.
On Friday, regional foreign ministers met in Tanzania ahead of the leaders’ summit. Kenyan Foreign Secretary Musalia Mudavadi described the talks as a "golden opportunity" to find a solution, advocating for the unification of previous peace processes hosted by Angola and Kenya.
After taking control of Goma last week, M23 fighters and Rwandan forces launched a new offensive on Wednesday, targeting the South Kivu town of Nyabibwe, located roughly 100 km (60 mi) from the regional capital Bukavu. This marked a breach of the unilateral humanitarian ceasefire declared earlier by M23, during which the group stated it had "no intention of taking control of Bukavu or other localities."
The United Nations reported on Wednesday that the battle for Goma resulted in at least 2,900 fatalities, a significantly higher toll than previously estimated.
Local and humanitarian sources revealed on Thursday that Congolese forces were preparing for an anticipated assault on Kavumu, a key town approximately 30 km from Bukavu that hosts the province’s airport. Troops and equipment were reportedly being evacuated to avoid capture by advancing M23 and Rwandan forces.
If Kavumu falls, it would represent another major blow to the Congolese government and military, further destabilizing a region plagued by decades of violence involving various armed groups.

 4 Min Read
4 Min Read